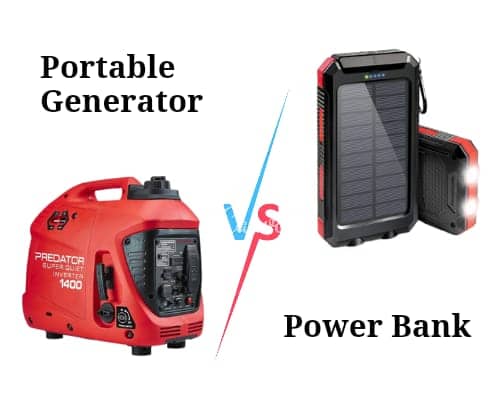
In an increasingly digital world, access to reliable power sources is more critical than ever. Whether it’s during an unexpected power outage, while camping in the wilderness, or simply on a long road trip, having a backup power solution can be a lifesaver. Two popular options for such situations are portable generators and power banks. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the key differences between these two backup power solutions to help you make an informed choice.
Generator vs. Power Bank
1. Portable Generators

Portable generators have been a staple for backup power for decades. They are versatile machines that generate electricity by burning fuel, typically gasoline or propane, to power electrical devices. Here are some key points to consider when it comes to portable generators:
Power Output: Portable generators come in various sizes and power capacities. They can provide a significant amount of electricity, making them suitable for running large appliances and even powering an entire home during an outage.
Runtime: The runtime of a portable generator depends on its fuel capacity. With a sufficient fuel supply, they can run for extended periods, making them ideal for long-term power needs.
Versatility: Portable generators can handle a wide range of power requirements, from running power tools at a construction site to keeping your home appliances operational during a blackout.
Noise Level: One drawback of portable generators is their noise level. They tend to be quite loud, which can be a nuisance in quiet settings or residential areas.
Maintenance: Maintenance is the lifeblood of generators, an intricate choreography of care and precision that orchestrates their longevity and unwavering reliability. Within this intricate ballet of mechanical marvels, oil changes and filter replacements stand as the crescendo of this routine.
Oil, akin to the lifeblood coursing through an engine’s veins, demands periodic renewal, a ritualistic changing of the guard to ensure peak performance. This liquid sentinel safeguards against the wear and tear of metal’s embrace, preserving the generator’s inner sanctum from the corrosive clutches of time.
Filters, the silent sentinels, act as gatekeepers, staunchly shielding the generator from foreign invaders. Their periodic replacement ensures the purest intake of air, fortifying the generator’s heart with the breath of unadulterated purity.
Proper maintenance is more than a routine; it is a covenant with reliability. It is the symphony that allows generators to sing with unwavering grace, ensuring their readiness when the call of power is at its zenith. In this ballet of maintenance, generators find their enduring encore, a testament to their enduring vitality.
Pros:
1. High Power Output: Portable generators can provide a significant amount of electricity, making them suitable for running large appliances and even powering an entire home during an outage.
2. Extended Runtime: With a sufficient fuel supply, generators can run for extended periods, making them ideal for long-term power needs.
3. Versatility: Generators can handle a wide range of power requirements, from running power tools at a construction site to keeping your home appliances operational during a blackout.
4. Reliable: When properly maintained, generators are highly reliable sources of backup power.
5. Wide Availability: Portable generators are readily available in various sizes and capacities.
Cons:
1. Noise Level: One major drawback of portable generators is their noise level. They tend to be quite loud, which can be a nuisance in quiet settings or residential areas.
2. Fuel Dependency: Generators require a constant supply of fuel, typically gasoline or propane, which can be expensive and inconvenient to store. They have ability to run whole night or day but they need refill time to time.
3. Maintenance: Generators require regular maintenance, including oil changes and filter replacements. Neglecting maintenance can lead to breakdowns.
4. Environmental Impact: Generators emit exhaust fumes and are not environmentally friendly.
2. Power Banks

Power banks, also known as portable chargers or battery banks, are compact devices designed to store electrical energy and deliver it to your devices when needed. They have gained popularity due to their convenience and portability.
Power Capacity: Power banks come in various capacities, measured in milliampere-hours (mAh) or watt-hours (Wh). While they can’t match the output of generators, they are suitable for charging smaller devices like smartphones, tablets, and laptops.
Portability: Power banks are incredibly portable and can easily fit in your pocket or bag. This makes them an excellent choice for on-the-go charging.
Silent Operation: Unlike generators, power banks operate silently, making them suitable for indoor use, camping, or any situation where noise is a concern.
Limited Runtime: The runtime of a power bank is limited by its capacity. Once it’s depleted, you’ll need to recharge it from a power source, which can be a drawback in extended power outage scenarios.
Low Maintenance: Power banks are virtually maintenance-free. You only need to recharge them regularly to keep them ready for use.
Pros:
1. Portability: Power banks are incredibly portable and can easily fit in your pocket or bag. This makes them an excellent choice for on-the-go charging.
2. Silent Operation: Unlike generators, power banks operate silently, making them suitable for indoor use, camping, or any situation where noise is a concern.
3. Low Maintenance: Power banks are virtually maintenance-free. You only need to recharge them regularly to keep them ready for use.
4. Environmentally Friendly: Power banks are rechargeable and produce no emissions, making them an eco-friendly choice.
5. Convenience: Power banks are convenient for charging small devices like smartphones, tablets, and laptops when you’re away from traditional power sources.
Cons:
1. Limited Power Output: Power banks have limited capacity and are not suitable for running large appliances or providing power for an extended period.
2. Limited Runtime: The runtime of a power bank is limited by its capacity. Once it’s depleted, you’ll need access to a power source to recharge it.
3. Device Compatibility: Power banks may not be compatible with all devices, and their charging speed can vary.
4. Not Suitable for High-Power Needs: If you need to power larger appliances or multiple devices simultaneously, a power bank may not be sufficient.
3. Choosing the Right Backup Power Solution
To determine whether a portable generator or a power bank is the right backup power solution for you, consider the following factors:
Power Requirements:
Assess your power needs. If you need to run large appliances or require power for an extended period, a portable generator is likely the better choice. On the other hand Power banks are more suitable for charging small devices. In short, if you want to run large size appliances at indoor or outdoor then portable generator is the best choice for you. Power bank is only dedicated to run only few appliances at outdoor.
Portability:
Think about where and how you plan to use the backup power source. If you need a solution for outdoor activities, traveling, or situations where noise is a concern, a power bank may be more convenient. This will be perfect when you power your small devices like mobile, laptop, tablets, and other small watt portable appliances.
Maintenance:
If you’re the person who can’t look after the generator, then the power bank is the perfect choice for you. Because generators require more maintenance than power banks, which are essentially plug-and-play devices.
Budget:
Generators can be a significant investment, because we get hard work with them like powering electric appliances or tools for long time period. While power banks are generally more affordable. While if you have low budget and need to power small devices for outdoor activities then power bank if good for you.
Environmental Impact:
Generators emit exhaust fumes and are not eco-friendly. If environmental concerns are a priority, power banks, which are rechargeable and produce no emissions, may be the better choice.
Conclusion
In the end, the choice between a portable generator and a power bank depends on your specific backup power needs and preferences. Both have their advantages and disadvantages, and the right solution for you will vary based on factors like power requirements, portability, maintenance, budget, and environmental considerations. By carefully assessing these factors, you can make an informed decision and ensure you have a reliable backup power source for when you need it most.
FAQs
When should I use a generator instead of a power bank?
Generators are typically used when you need to power larger appliances, tools, or provide backup power for an extended period during a power outage. They are suitable for situations where a high wattage output is required.
When is a power bank more suitable than a generator?
Power banks are ideal for charging small electronic devices like smartphones, tablets, and laptops on the go. They are convenient for short-term power needs when you don’t have access to a power outlet.
Are generators or power banks more portable?
Power banks are generally more portable and lightweight than generators, making them easier to carry in your backpack or pocket.
Which one is more environmentally friendly, a generator or a power bank?
Power banks are considered more environmentally friendly because they do not produce emissions or require fuel. Generators, depending on the type and fuel source, can emit exhaust gases and have a larger carbon footprint.
Can a generator be used for off-grid living or camping?
Yes, generators are commonly used for off-grid living and camping to power appliances, lights, and other equipment. They provide a reliable source of electricity in remote areas.
Do power banks require maintenance like generators?
Power banks generally require less maintenance than generators. You need to recharge them regularly, but there are no oil changes, fuel refills, or other maintenance tasks required.
Which one is more cost-effective in the long run, a generator or a power bank?
Power banks are usually more cost-effective for charging small devices, while generators are better suited for larger power needs. The cost-effectiveness depends on your specific power requirements.
Can a power bank be used as a backup for a generator?
Yes, you can use a power bank as a secondary backup for a generator. This ensures that you have a portable source of power for small devices even if the generator runs out of fuel or experiences issues.
Are there any safety considerations when using generators or power banks?
Yes, both generators and power banks have safety considerations. Generators should be used in well-ventilated areas to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning, and power banks should be charged with certified chargers and stored away from extreme heat or moisture to prevent overheating or damage.