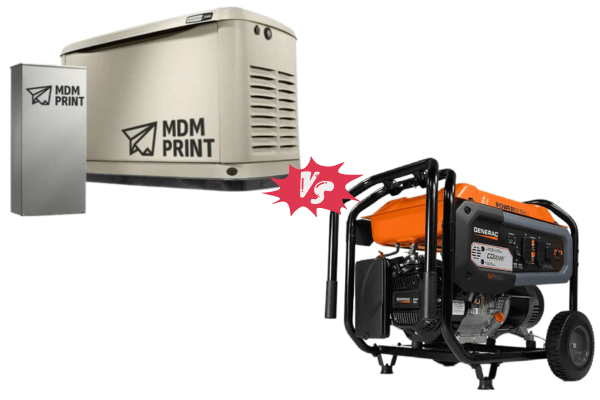
When it comes to ensuring a reliable power supply for your home, especially during unexpected outages, generators play a crucial role. However, choosing the right type of generator can be a daunting task.
Two popular options are portable generators and standby generators, each offering unique benefits and features. In this blog post, we will compare Portable Generators vs. Standby Generators, exploring their differences, advantages, and considerations to help you make an informed decision for your home.
Portable Generators vs. Standby Generators
Portable Generators: Power on the Move
Portable generators are versatile and convenient power solutions. They are typically compact, lightweight, and designed to be easily moved from one location to another. Portable generators are fueled by gasoline, propane, or diesel, and they offer a range of power outputs to suit different needs.
Advantages of Portable Generators:
In addition to the advantages mentioned, portable generators offer some unique and deep benefits that make them a valuable power solution in various situations. Here are some additional insights:
Emergency Preparedness: Portable generators play a crucial role in emergency preparedness. During power outages caused by natural disasters like hurricanes, storms, or earthquakes, they can provide a reliable source of electricity to keep essential appliances running, such as refrigerators, sump pumps, or medical equipment. Being able to maintain power supply during emergencies can help ensure safety, comfort, and even save lives.
Remote Locations: Portable generators are ideal for powering devices and equipment in remote locations where access to the electrical grid is limited or unavailable. For example, when camping or engaging in outdoor activities, portable generators can provide a convenient source of electricity for lighting, cooking appliances, charging electronic devices, or running small appliances. This allows individuals to enjoy the benefits of modern technology and convenience even in remote or off-grid areas.
Tailgating and Outdoor Events: Portable generators are a popular choice for tailgating parties, outdoor events, or gatherings. They can power speakers, lighting systems, grills, fans, and other entertainment equipment, enhancing the overall experience for participants. With a portable generator, you can create a comfortable and enjoyable atmosphere at outdoor gatherings without worrying about access to electrical outlets.
Job Sites and Construction Projects: Portable generators are frequently utilized in job sites and construction projects. They provide a reliable power source to operate power tools, lights, compressors, and other equipment necessary for the construction or renovation process. The portability of these generators allows them to be easily moved around the site, ensuring flexibility and convenience.
Recreational Vehicles (RVs) and Boating: Many portable generators are specifically designed to cater to the power needs of recreational vehicles and boats. These generators can be easily mounted on RVs or boats, providing electricity for lighting, appliances, air conditioning, and charging batteries. Portable generators offer the freedom to explore and travel without worrying about access to power hookups or being limited by the availability of electrical infrastructure.
Noise Reduction Technology: Portable generators have witnessed advancements in noise reduction technology. Many models now feature quieter operation, making them suitable for various applications where noise levels need to be kept to a minimum. This is especially important in camping grounds, neighborhoods, or any location where noise regulations are in place. Quieter operation ensures a more pleasant and considerate experience for users and their surroundings.
Fuel Options: Portable generators come in a range of fuel options, including gasoline, diesel, propane, or even solar-powered models. This variety allows users to choose a generator that aligns with their preferences, fuel availability, and environmental considerations. Solar-powered portable generators, for instance, provide a sustainable and renewable energy option for those seeking to reduce their carbon footprint.
Considerations for Portable Generators:
Power Management: Due to their limited power output, it becomes crucial to prioritize and manage the electrical load when using a portable generator. Identifying essential appliances and systems that require power, such as refrigerators, heating or cooling equipment, and medical devices, is essential to ensure efficient utilization of the available power.
Load Balancing: When operating a portable generator, it’s important to distribute the electrical load evenly across different circuits or appliances. Uneven load distribution can lead to overload, tripped circuit breakers, and potential damage to both the generator and the connected devices. Proper load balancing helps optimize the generator’s performance and prevents unnecessary strain.
Noise Considerations: Portable generators can generate a significant amount of noise during operation, which can be a concern, particularly in residential areas or during camping trips. It’s important to check the noise levels of the generator and consider factors like noise restrictions, proximity to neighbors, and local regulations to ensure a quieter and more peaceful environment.
Emissions and Environmental Impact: Different types of portable generators have varying levels of emissions. Gasoline-powered generators tend to emit more pollutants compared to propane or diesel-powered ones. When choosing a portable generator, it’s worth considering the environmental impact and opting for models that adhere to emission regulations or provide cleaner energy alternatives.
Safety Measures: Operating a portable generator comes with inherent safety risks. It’s crucial to follow safety guidelines, such as keeping the generator outdoors in a well-ventilated area to prevent carbon monoxide buildup, using proper grounding techniques to avoid electric shocks, and ensuring the generator is protected from the elements to prevent damage or malfunctions.
Maintenance and Longevity: Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the longevity and reliability of a portable generator. This includes tasks like changing the oil, inspecting and cleaning filters, checking fuel levels and connections, and conducting periodic load tests. Proper maintenance can help prevent breakdowns, extend the generator’s lifespan, and ensure it functions optimally when needed.
Transfer Switch Considerations: When connecting a portable generator to your home’s electrical system, it’s recommended to use a transfer switch. A transfer switch allows for safer and more convenient switching between the generator and the utility power. It also helps prevent backfeeding, which can pose a danger to utility workers and damage your generator or appliances if not properly managed.
Portability and Storage: As the name suggests, portability is one of the main advantages of these generators. Consider the weight, size, and maneuverability of the generator, especially if you plan to transport it frequently or use it for camping or outdoor activities. Additionally, proper storage is essential to protect the generator from harsh weather conditions and ensure it remains in good working condition over time.
By taking these considerations into account, you can make informed decisions when selecting, operating, and maintaining a portable generator to meet your specific power needs and ensure a safe and efficient power supply during emergencies or outdoor adventures.
Standby Generators: Reliable Power Backup
Standby generators, also known as whole-house generators, are permanently installed outside your home and provide seamless backup power during outages. They are connected to your home’s electrical system and fueled by natural gas or propane, ensuring a continuous power supply.
Advantages of Standby Generators:
Automatic Load Management: Standby generators often come equipped with automatic load management systems. These systems monitor the power usage in your home and distribute the available generator power accordingly. They prioritize essential loads, such as heating and cooling systems, refrigeration, and medical equipment, ensuring that critical functions are maintained even during an outage. This intelligent load management helps optimize the generator’s performance and prevents overload situations.
Remote Monitoring and Control: Many modern standby generators offer remote monitoring and control capabilities. Through a mobile app or a web-based interface, homeowners can conveniently monitor the generator’s status, fuel levels, and maintenance requirements from anywhere. They can also start or stop the generator remotely, adjust settings, and receive real-time notifications about power outages and generator operation. This feature adds an extra layer of convenience and peace of mind for homeowners.
Advanced Transfer Switches: Standby generators are typically connected to an automatic transfer switch (ATS), which detects when there is a loss of utility power and automatically switches the electrical load from the main power supply to the generator. Advanced transfer switches provide additional functionalities, such as load shedding and load sequencing. Load shedding allows the ATS to prioritize critical loads and temporarily shed non-essential ones during a power shortage, ensuring that vital appliances receive power first. Load sequencing enables a staged startup of large appliances, reducing the initial power demand when the generator kicks in.
Exercise Modes: Standby generators require regular exercise to maintain optimal performance. Exercise modes allow the generator to run for a short period at scheduled intervals, typically once a week. During exercise mode, the generator operates under a lighter load, ensuring that it remains in good working condition. This feature also helps identify any issues or faults in the system before they become significant problems, improving reliability and longevity.
Noise Reduction Technology: Traditional generators can be noisy, but standby generators often come with advanced noise reduction technology. They are designed with sound-dampening materials and mufflers to minimize operational noise levels. This feature is particularly important for residential areas where noise regulations may be in place. With quieter operation, standby generators are less likely to disturb neighbors or cause noise-related issues.
Professional Installation and Maintenance: Standby generators require professional installation by certified technicians. During installation, the generator is connected to the home’s electrical system and fuel source, ensuring seamless integration and safe operation. Additionally, regular maintenance by professionals is crucial to keep the generator in optimal condition. Maintenance tasks may include inspecting and testing the generator, changing filters, and checking fuel levels. Professional installation and maintenance help maximize the lifespan and reliability of the standby generator.
Environmental Considerations: Standby generators fueled by natural gas or propane offer environmental benefits compared to gasoline or diesel-powered generators. Natural gas and propane are cleaner-burning fuels, resulting in lower emissions of pollutants such as carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter. Furthermore, these generators eliminate the need for storing large amounts of gasoline or diesel fuel, reducing the risk of spills and contamination.
By combining these unique features and technologies, standby generators provide homeowners with a reliable and hassle-free power backup solution, ensuring comfort, safety, and peace of mind during power outages.
Considerations for Standby Generators:
Standby generators, also known as backup generators, provide a reliable source of electricity during power outages or emergencies. Here are some unique and deep considerations regarding standby generators:
Load Calculation: Before installing a standby generator, it’s crucial to perform a load calculation to determine the power requirements of your home. This involves assessing the electrical needs of various appliances, electronics, and systems to ensure the generator can handle the load adequately. A professional electrician can help you with this calculation to ensure the generator’s capacity matches your needs.
Fuel Type Options: Standby generators can be powered by different fuel types, including natural gas, propane, and diesel. Each fuel type has its advantages and considerations. Natural gas is often the most convenient option for residential use as it is readily available through utility lines. Propane offers increased fuel storage options and is suitable for areas without natural gas access. Diesel generators are known for their durability and long-term fuel storage capabilities, making them suitable for remote locations or prolonged power outages.
Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS): Standby generators are typically equipped with an automatic transfer switch, which monitors the utility power supply. When a power outage is detected, the ATS automatically disconnects the home from the utility grid and activates the generator. Once utility power is restored, the ATS transfers the load back to the grid and shuts down the generator. This seamless transition ensures uninterrupted power supply without manual intervention.
Noise Considerations: Standby generators are designed to operate quietly, but they still produce some level of noise. The noise level can vary depending on the generator’s size, design, and enclosure. If noise is a concern, you can explore options like soundproof enclosures or selecting a generator with a lower decibel rating. It’s important to review the manufacturer’s specifications and consider local noise regulations when choosing a standby generator.
Environmental Impact: Standby generators can have an environmental impact, especially if they run on fossil fuels. However, advancements have been made in generator technology to minimize emissions and improve fuel efficiency. Some generators are designed to meet strict emission standards and incorporate features like low-idle mode to conserve fuel when the electrical load is minimal. Additionally, exploring greener fuel options such as biogas or biodiesel can further reduce the environmental footprint of standby generators.
Compliance with Local Codes: Installing a standby generator requires compliance with local building codes and regulations. These codes vary from region to region and often cover aspects such as generator placement, fuel storage, noise limits, and electrical connections. Hiring a licensed electrician who is familiar with local codes ensures that the installation meets all necessary requirements and safety standards.
Remote Monitoring and Control: Modern standby generators often come equipped with remote monitoring and control capabilities. Through smartphone apps or web interfaces, you can monitor the generator’s status, fuel levels, and even start or stop it remotely. This feature provides added convenience and peace of mind, allowing you to manage your generator from anywhere.
By considering these factors, you can make informed decisions when it comes to installing and maintaining a standby generator for your home. It’s essential to consult with professionals and reputable generator manufacturers to ensure the system meets your specific needs and requirements.
Choosing the Right Generator for Your Home
When deciding between portable and standby generators, consider the following factors:
Noise Level: Standby generators are usually quieter compared to portable generators, which can be important if you live in a densely populated area or have noise restrictions.
Fuel Type: Determine the fuel type that best suits your needs and availability. Standby generators often run on natural gas or propane, which may require a connection to the gas line or the installation of a propane tank. Portable generators typically run on gasoline or diesel, which are more readily available but may require additional fuel storage.
Automatic Operation: Consider the convenience of automatic operation. Standby generators can detect a power outage and automatically start, providing a seamless transition to backup power. Portable generators require manual startup and connection to your home’s electrical system.
Power Management Features: Assess the power management features offered by the generator. Some standby generators come with load management systems that prioritize essential circuits, preventing overload and allowing for efficient power distribution.
Maintenance: Evaluate the maintenance requirements of the generator. Standby generators often require professional maintenance at regular intervals, while portable generators may have simpler maintenance needs that can be performed by the owner.
Warranty and Service: Research the warranty and service options provided by the generator manufacturer. Consider the length of the warranty, availability of service centers, and customer support.
Safety Features: Ensure that the generator has adequate safety features, such as circuit breakers, grounding mechanisms, and low-oil shutoffs. Standby generators are typically installed by professionals who ensure compliance with safety standards.
Transfer Switch: Determine if a transfer switch is required for your generator. Standby generators usually require a transfer switch to connect the generator to your home’s electrical system. Portable generators may require a manual transfer switch or individual cords to power specific appliances or circuits.
Conclusion
Choosing the right generator for your home depends on your power requirements, budget, and preferences. Portable generators offer convenience, affordability, and versatility, while standby generators provide higher power outputs, seamless operation, and long-term backup power.
Assess your needs and consult with a professional to determine the most suitable generator type for your home. With the right choice, you can ensure a reliable power supply and peace of mind during unexpected outages.